Nuclear fusion has long been considered a scientific frontier. Today, it’s entering a new phase - one defined by engineering milestones, commercial ambition, and accelerating capital flows. As global energy demand accelerates driven by population growth, expanding middle classes, and the electrification of new sectors such as AI, renewables alone are unlikely to meet future needs. Fusion offers a compelling pathway to clean, dispatchable power at scale.
This whitepaper, jointly published by TRIREC and the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), explores the evolving fusion landscape through both technological and commercial lenses. It distils the latest scientific breakthroughs, investment trends, and policy developments, while highlighting the practical challenges that must be addressed to bring fusion technologies to market.
Key Insights
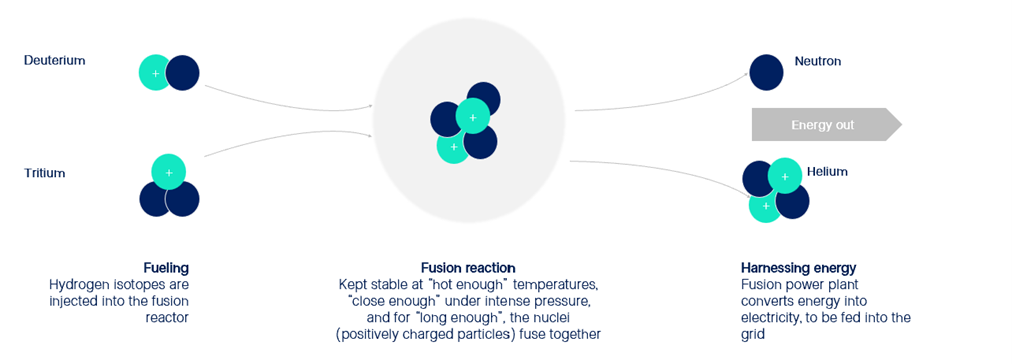
Fusion Science - The whitepaper introduces the core technological approaches - Magnetic Confinement Fusion (MCF), Inertial Confinement Fusion (ICF), and Magnetised Inertial Fusion (MIF) - and highlights recent breakthroughs, including the world’s first Q_sci > 1 result at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory.
Investment Momentum - Over US$8bn in private capital has flowed into fusion since 2021, with over US$2.2bn raised in 2025 alone. Leading companies such as Commonwealth Fusion Systems, Energy Singularity, Tokamak Energy, Type One Energy, TAE Technologies, Ex-Fusion, and Zap Energy are achieving record milestones and accelerating the path to commercialisation.
Global Race and Collaboration - The US, China, and UK are spearheading national efforts, with ambitious targets for demonstration and commercial fusion plants in the 2030s and 2040s. International partnerships and supply chain development are critical to overcoming technical and regulatory hurdles.
Challenges Remain - Despite significant progress, technical, commercial, and policy challenges persist - including plasma stability, tritium supply, material durability, regulatory frameworks, and talent shortages. Patient, long-term capital and cross-sector collaboration will be essential.
Expert Perspectives - The whitepaper features candid and diverse views from global leaders in utilities, academia, and industry on the timeline, risks, and opportunities for fusion energy.
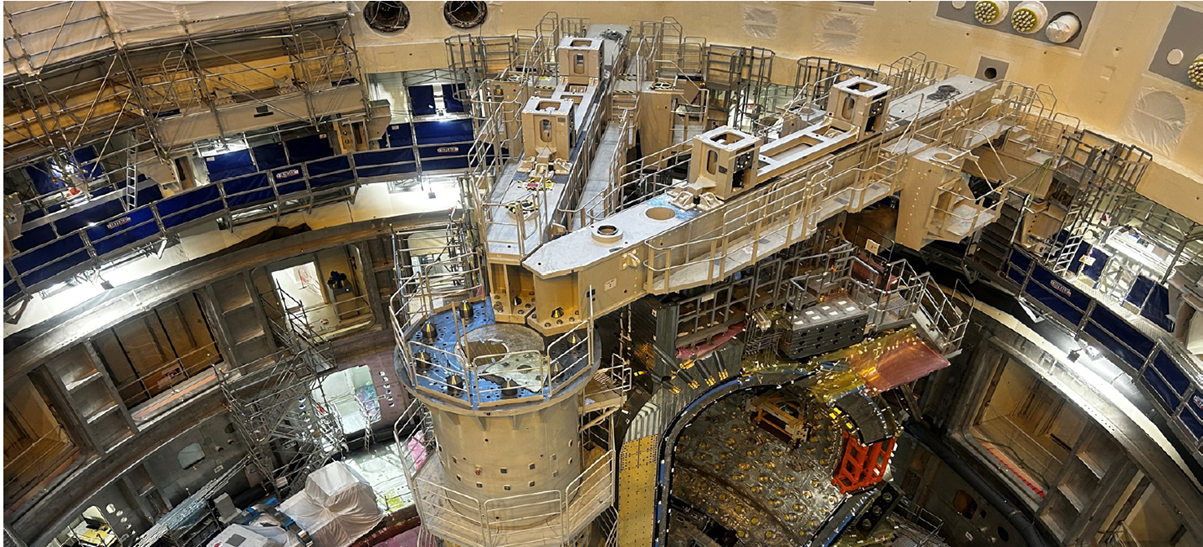
Interior of the ITER tokamak in France - one of the most advanced international nuclear fusion research and engineering projects. Credit ITER Organization, http://www.iter.org/
Acknowledgements
This whitepaper is the result of a collaborative effort between TRIREC and the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), Singapore. We are extremely grateful for the contributions of our research partners, expert interviewees, and all those who provided insights and feedback throughout the development of this publication.